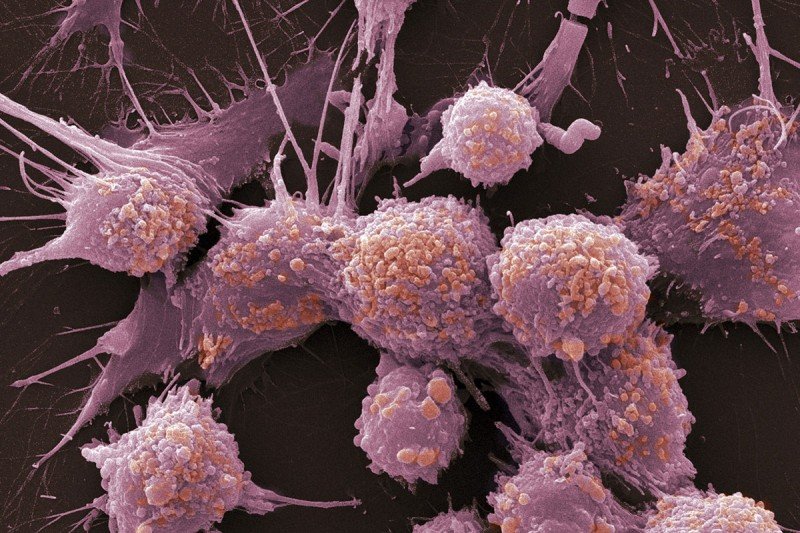
PC3 human prostate cancer cells, stained with Coomassie blue, under differencial interference
Prostate cancer (PCa) is the most commonly diagnosed malignancy and the second leading cause of cancer deaths in the western male population 1.Annual prostate cancer diagnoses worldwide are.
Prostate cancer cells Nikon’s Small World
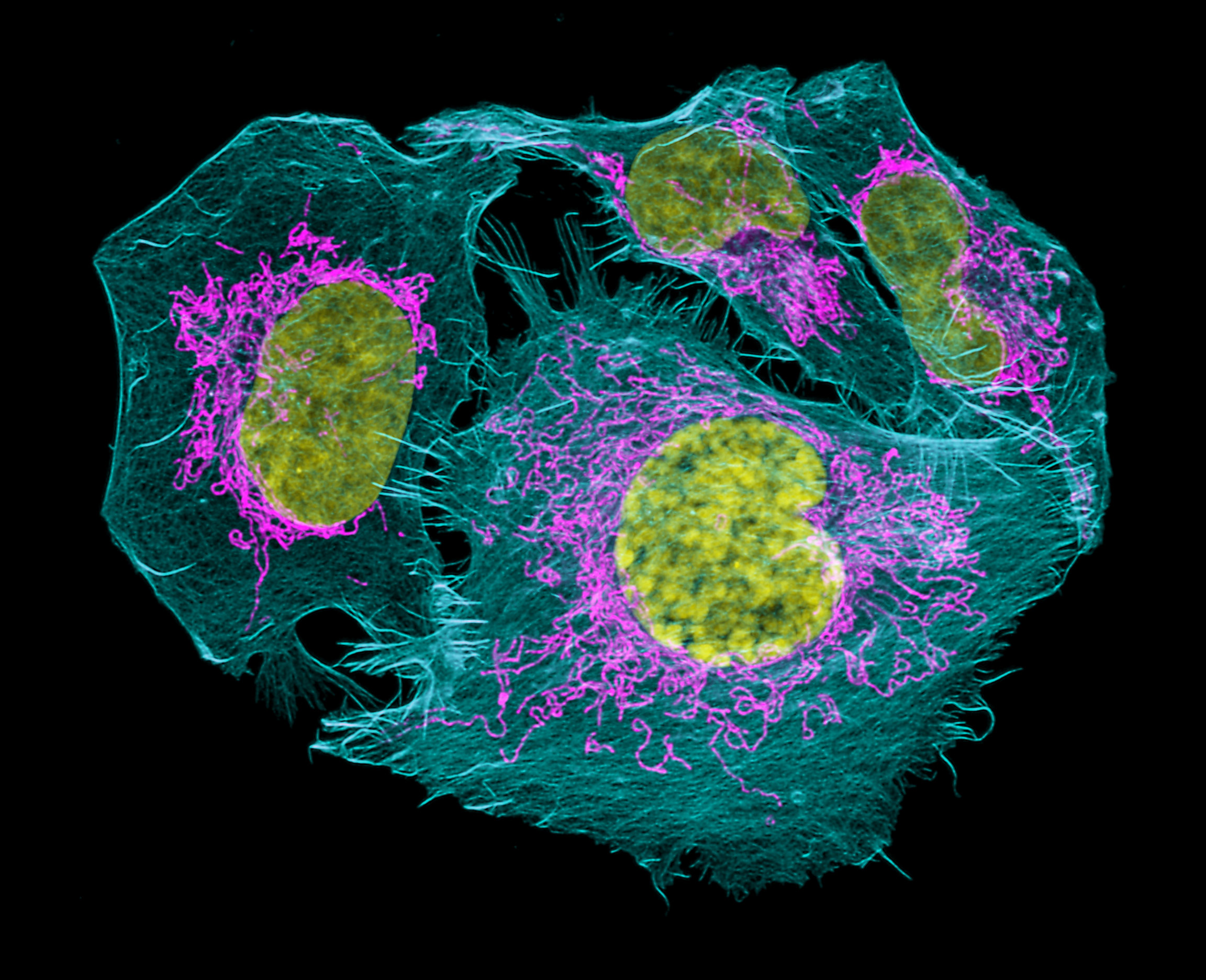
Background Regulator of chromosome condensation 2 (RCC2) was a telophase disk-binding protein on mitosis, and functions as an oncogene in many human cancers. However, its role on prostate cancer (PCa) was unknown. The goal of this study is to explore the function of RCC 2 on PCa development. Methods The expression of RCC2 and its methylation level, its correlation with lymph node metastasis or.
PC3 human prostate cancer cells, stained with Coomassie blue, under differencial interference
On the simplest level, this scoring system assigns a number from 6 to 10 to describe how abnormal the cells appear under a microscope. A score of 6 means the cancer cells still look very much like normal cells and pose little danger of spreading quickly. A score of 8 to 10 indicates that the cancer cells have very few features of a normal cell.
PC3 human prostate cancer cells, stained with Coomassie blue, under differencial interference
As previously mentioned, the only way to confirm PCa currently is through an image-guided prostate biopsy procedure. The biopsy specimens obtained during the procedure are examined under a microscope to assign them a primary, secondary, and total Gleason score, which is a measure of cell differentiation and cancer aggressiveness (Fig. 1B.
Prostate Cancer, Light Micrograph Stock Photo Image of carcinoma, stain 183041036

Under the microscope, cancer cells were found. The cancer had a Gleason score of 7. A Gleason score is a way of describing prostate cancer based on how abnormal the cancer cells in a biopsy sample look under a microscope. It also predicts how quickly the cancer cells are likely to grow and spread.
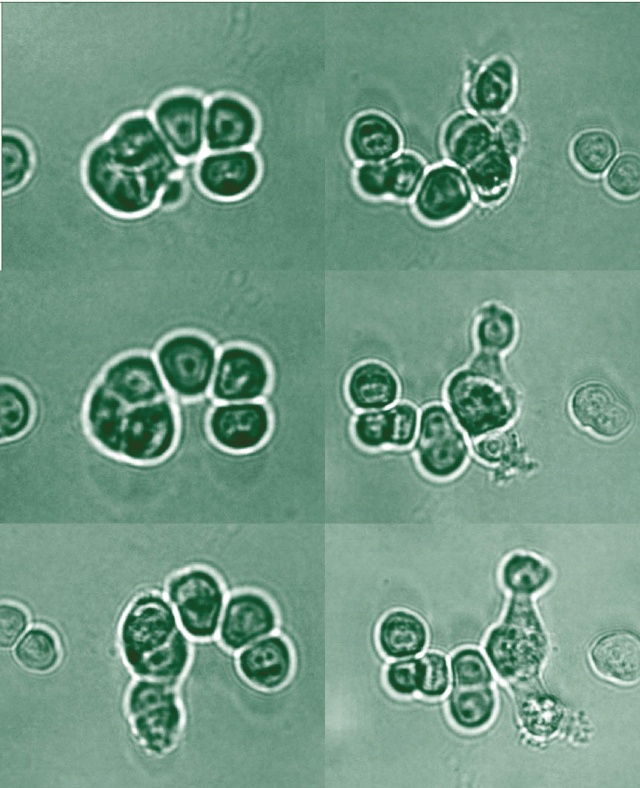
Prostate cancer cell line PC3 after etoposide treatment. Apoptotic... Download Scientific Diagram

Intraoperative evaluation of specimens during radical prostatectomy using frozen sections can be time and labor intensive. Nonlinear microscopy (NLM) is a fluorescence microscopy technique that.
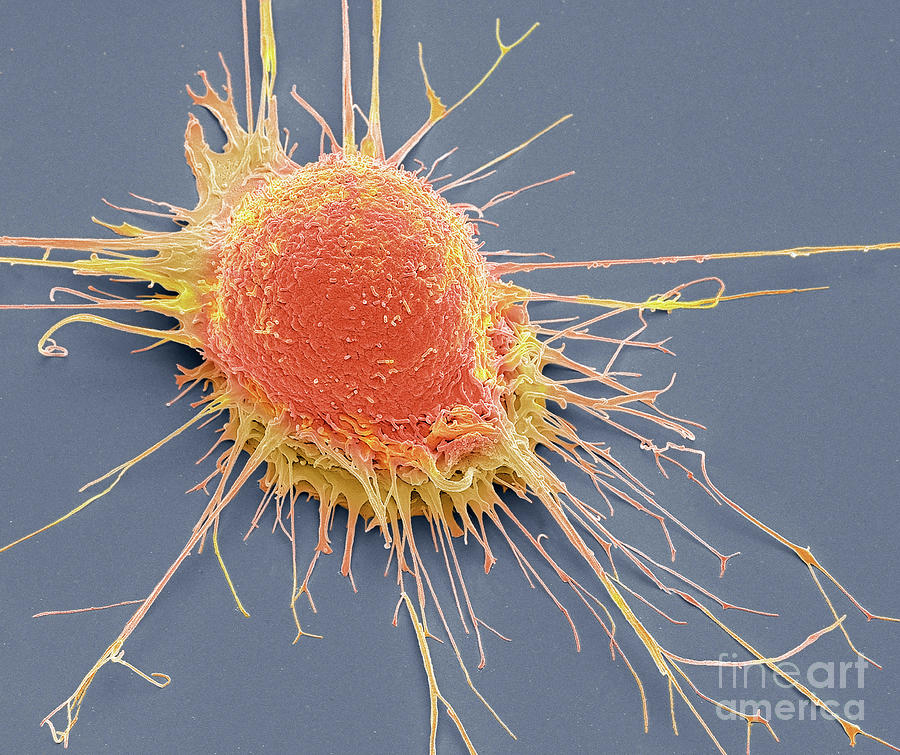
Prostate cancer cells, SEM Stock Image F027/0571 Science Photo Library

Inverted capsule embedding was used to study archival metastatic prostate in pelvic nodes and Du145 cell line in a monolayer culture. Results: Staining for CD133 positively identified stem cells that were found in benign prostatic hyperplasia, benign prostate, and prostate cancer cells. Paraffin embedded sections showed a single type of stem.
PSMA A New Target for Prostate Cancer Treatment Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center
Tissue biopsy/prostatectomy samples, visualized by transmission electron microscopy, identified that metastatic cells are a lineage of stem cells, which have dedifferentiated into cancerous columnar/cuboidal cells. These cells demonstrate nuclear plasticity; the loss of nuclear membranes and boundary between nucleus and cytoplasm; and the.
Prostate cancer cells, SEM Stock Image C001/8166 Science Photo Library

Differentiation refers to how "normal" a cancer cell looks under a microscope when compared to a normal prostate cell. Poorly differentiated or undifferentiated: The cancer cells look much different than normal, healthy cells. Well differentiated: The cancer cells look similar to normal, healthy cells.
Prostate Microscopy Advanced Imaging and Analysis Techniques

Prostate cancer (PCa) is the most commonly diagnosed (non-cutaneous) cancer among men in the United States 1.According to the National Institute of Health SEER report, over 3.25 million men in the.
Science Is Art Prostate cancer cells under the microscope What's Up at Upstate SUNY Upstate
Some of the most common IHC stains used for definitive prostate cancer diagnosis include p63 and high-molecular-weight cytokeratin (HMWCK), which selectively label basal cells in prostate tissue [21, 22]. p63 is a homologue of the tumor suppressor gene p53, and HMWCK reacts with the monoclonal antibody keratin 34BE12, both of which are present in the basal layer of prostatic glands [23, 24].
Prostate Cancer Cell Photograph by Steve Gschmeissner/science Photo Library Pixels
The cancer cells look like healthy cells. Stage II: The tumor is found only in the prostate. PSA levels are medium or low. Stage II prostate cancer is small but may have an increasing risk of growing and spreading. Stage IIA: The tumor cannot be felt and involves half of 1 side of the prostate or even less than that.
Prostate Microscopy Advanced Imaging and Analysis Techniques

As normal prostate cells turn into tumor cells, their appearance changes under the microscope. The pathologist assigns the prostate cancer a Gleason score on a scale of 1 to 5 based on how much the cancer looks like healthy prostate tissue. The higher the Gleason score, the more abnormal the cancer cells appear. The pathologist first scores the.
Prostate cancer of a human stock photo. Image of morphology 66313424

The tests and scans you have to diagnose prostate cancer give information about: the type of cell the cancer started in and where it began; how abnormal the cells look under the microscope (the grade) the size of the cancer and whether it has spread (the stage) In the UK, doctors use the Grade Groups or Gleason score to grade prostate cancer.
Prostate cancer cell, coloured scanning electron micrograph. — diagnosis, malignant Stock

B cells. T cells are not the only immune population under consideration for mediating immunological treatment effectiveness. There is also a greater abundance of B cells in PCa compared to benign prostatic tissues, and the influx of B cells into the prostate TME has been linked with more aggressive disease (Woo et al. 2014, Wu et al. 2020).B cells, following their recruitment, can produce.
Research Shipley Prostate Cancer Research Center

Prostate Pathology. When your prostate was biopsied, the samples taken were studied under the microscope by a specialized doctor with many years of training called a pathologist. The pathologist sends your doctor a report that gives a diagnosis for each sample taken. Information in this report will be used to help manage your care.