Rocket Engine Static Testing with Thrust Vector Control YouTube

Thrust vectoring as the name suggests is the science that controls the direction of the thrust. It is one of the technologies in the aviation industry that is being extensively used in modern aircraft like F-22, F-35 and Sukhoi-35 and will probably become more advanced in the coming years. It is achieved with the help of a modular nozzle that.
Figure 1 from Thrust Vector Control for Nuclear Thermal Rockets Semantic Scholar

At that point the first stage drops off, lightening the vehicle, and the second stage ignites and accelerates the vehicle further. Most space launch vehicles have three stages. See also launch vehicle. Other articles where thrust-vector control is discussed: rocket and missile system: Design principles:.its engines is known as thrust-vector.
How Does a Rocket Work? An Explanation of Rocket Science Owlcation
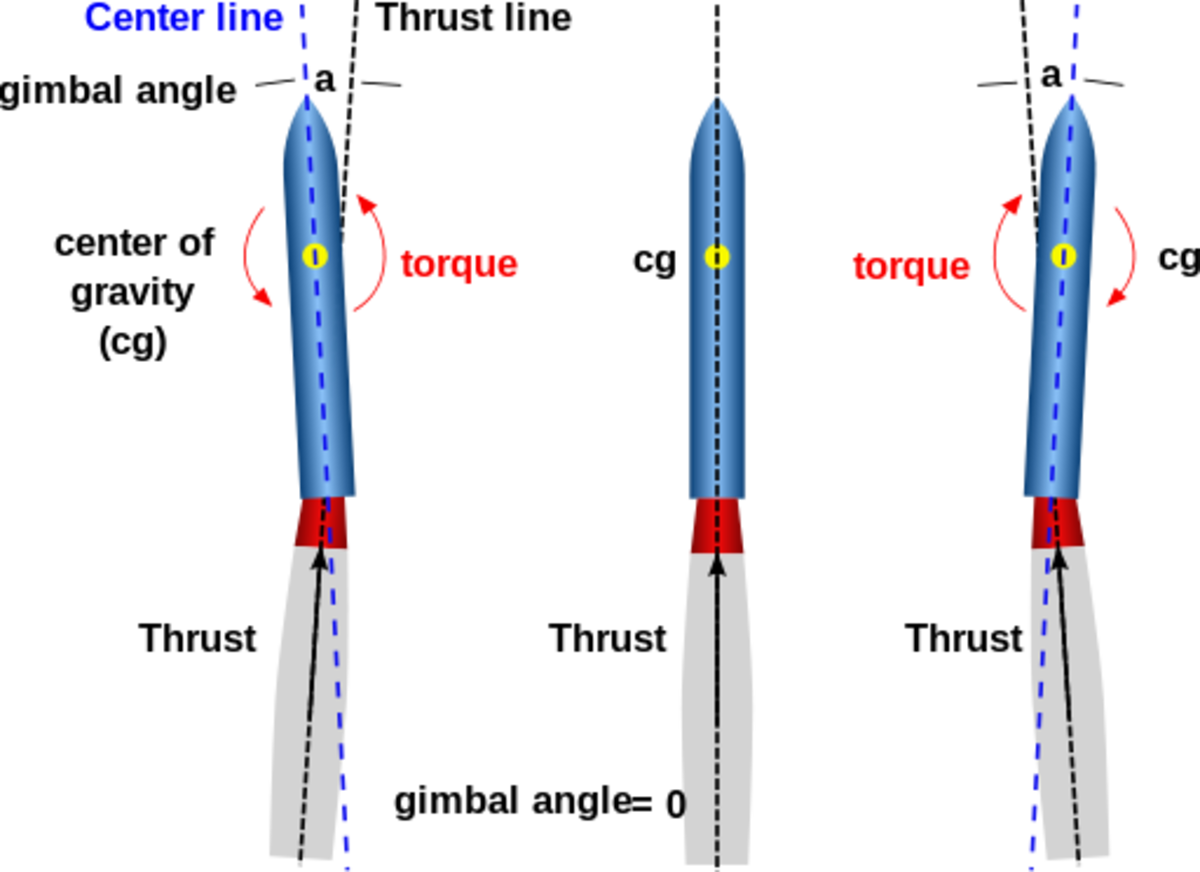
Abstract. An efficient propulsion system holds the key to the smooth operation of any aerospace vehicle over different flight regimes. Apart from generating the necessary thrust, emphasis has also been laid on vectoring the direction of thrust. The primitive modes of thrust vectoring chiefly focused on mechanical means such as the use of gimbals or hinges. The current state-of-the-art.
3. ThrustVector Control System of a Rocket A
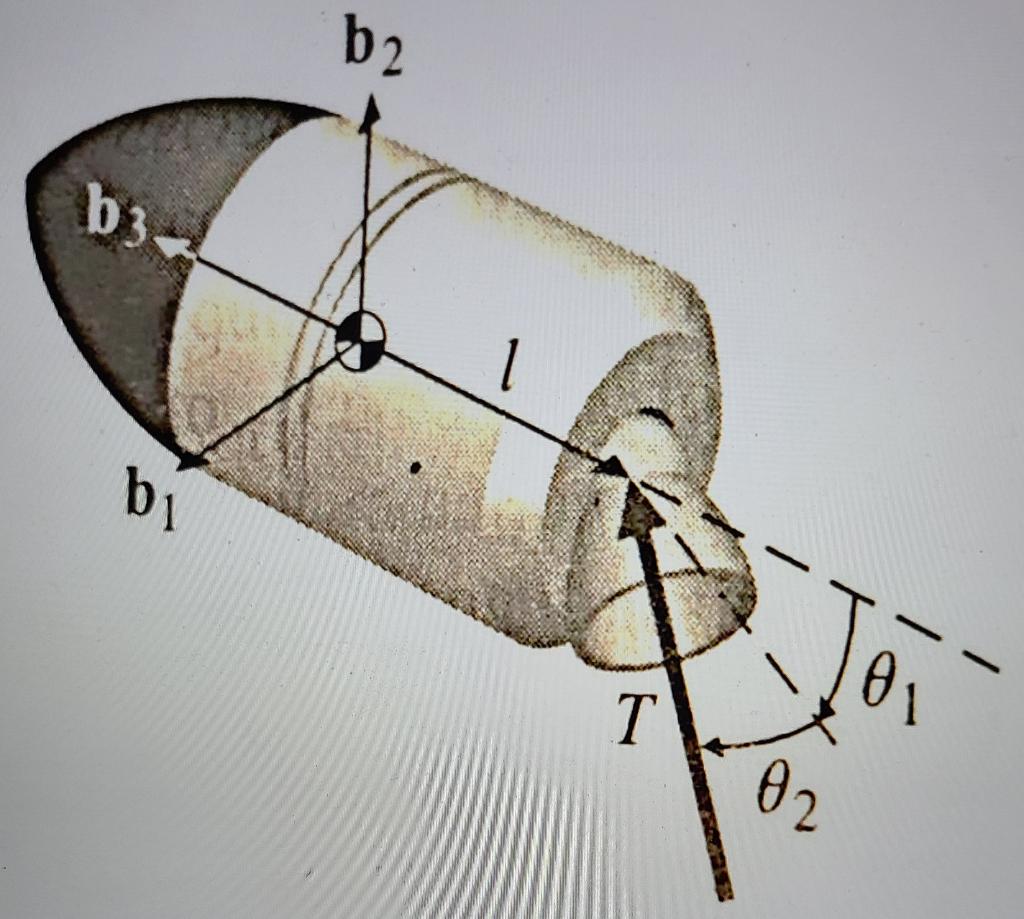
Thrust Vectoring Mechanism: The thrust vectoring mechanism is the heart of the thrust vector control engine. It allows for the manipulation of the engine's exhaust direction . This mechanism can be achieved through various methods , including mechanical linkages, hydraulic actuators, or even advanced computer-controlled systems .
THRUST VECTORING NOZZLE FOR MILITARY AIRCRAFT ENGINES Semantic Scholar

Thrust vector control (TVC) is used for low-speed maneuvering and the landing legs deploy shortly before touch-down with mechanism to dissipate the landing energy. 3 Review of key mechanism design divers. International competition and developments are ongoing aiming to reduce the cost of access to space. One of the key cost reduction drivers is.
Aerospace Free FullText Mathematical Modelling and Fluidic Thrust Vectoring Control of a

Thrust vectoring nozzles play a crucial role in the field of aerospace engineering, particularly in the design and optimization of propulsion systems.These innovative nozzles allow for enhanced maneuverability and control of aircraft, rockets, and jet engines.In this deep dive, we will explore the concept of thrust vectoring nozzles, delve into their design aspects, and understand their.
Thrust Vectoring for Water Rocket (3D Printed) YouTube
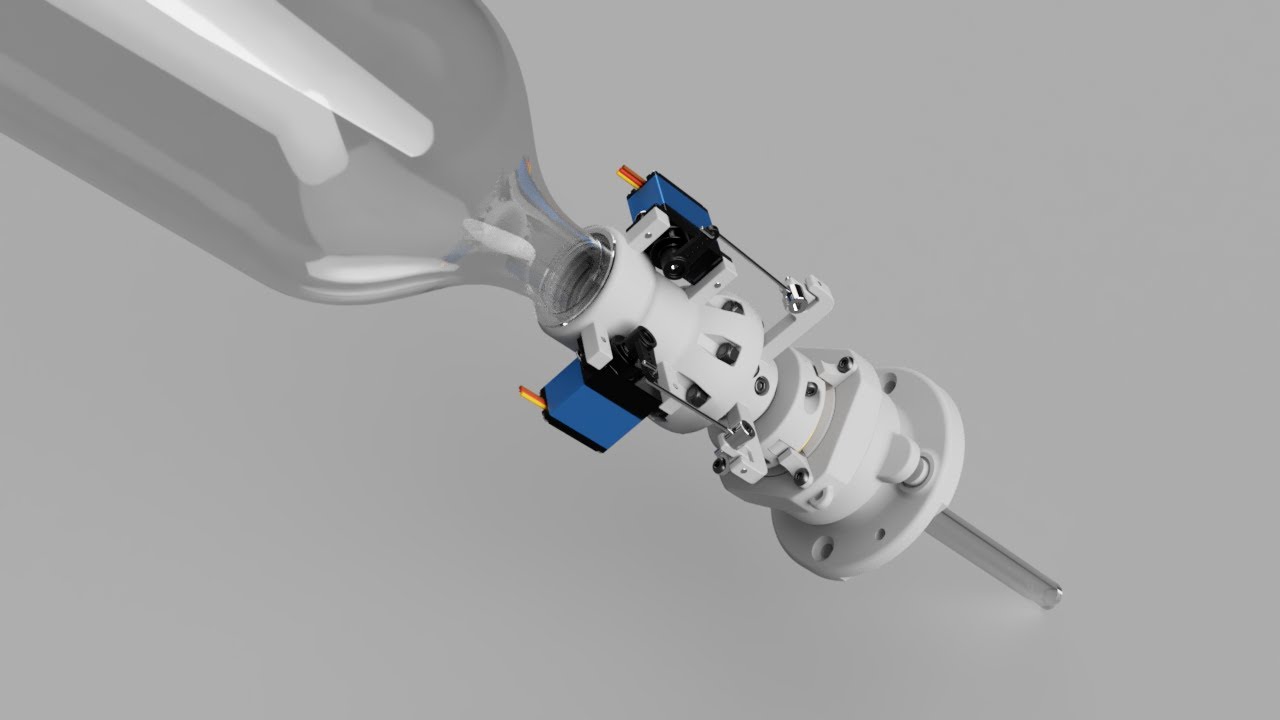
TVC, or thrust-vector-control, is a technique used in rocketry to control the thrust of a rocket. By controlling its propulsive force, we obtain full command over its orientation.
Thrust vector control for (a) yawing; (b) rolling; and (c) pitching. Download Scientific Diagram

Thrust vectoring control (TVC) is an advanced control technique that has been used in many supersonic air vehicles (Francis 2018).TVC can change the axis of thrust and offer pitching, yawing, and rolling momentums, as portrayed in Fig. 1.Figure 2 shows the classification of the TVC, namely mechanical TVC (M-TVC) and fluidic TVC (F-TVC). Numerous mechanical actuators enhance the superfluous.
Thrust vectoring

This paper is the third installment in a seven-paper series surveying the design, engineering, test validation, and flight performance of the Core Stage Thrust Vec- tor Control system. In this paper, a new method of modeling rocket vehicle thrust vectoring servoelastic dynamics is presented.
Thrust Vector Control Series E Hold Down YouTube

A thrust vector control system is used in air vehicles to manipulate the axial thrust and give it attitude control. This type of system is useful when the air control systems prove to be inefficient at higher altitudes. The inspiration for this work was to develop a Thrust Vector Control System prototype that occupies minimum space and can be.
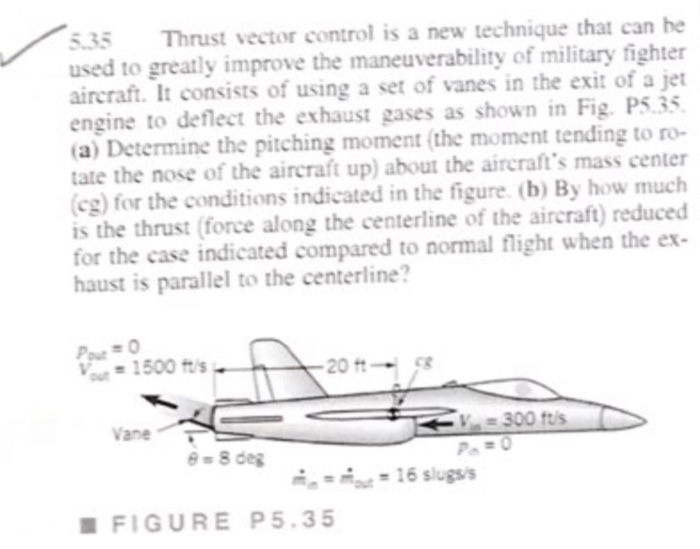
Solved 5.35 Thrust vector control is a new technique that
19.17.1 Space Shuttle Main Engine Thrust Control. Control of the thrust from the three main engines is crucial during the launch of the space shuttle. A pair of linear actuators is positioned to allow rotation of the engine or the nozzle on its bearings along orthogonal planes to move the resulting thrust vector.
Here Is How Thrust Vectoring Works & Why It's An Amazing Pie
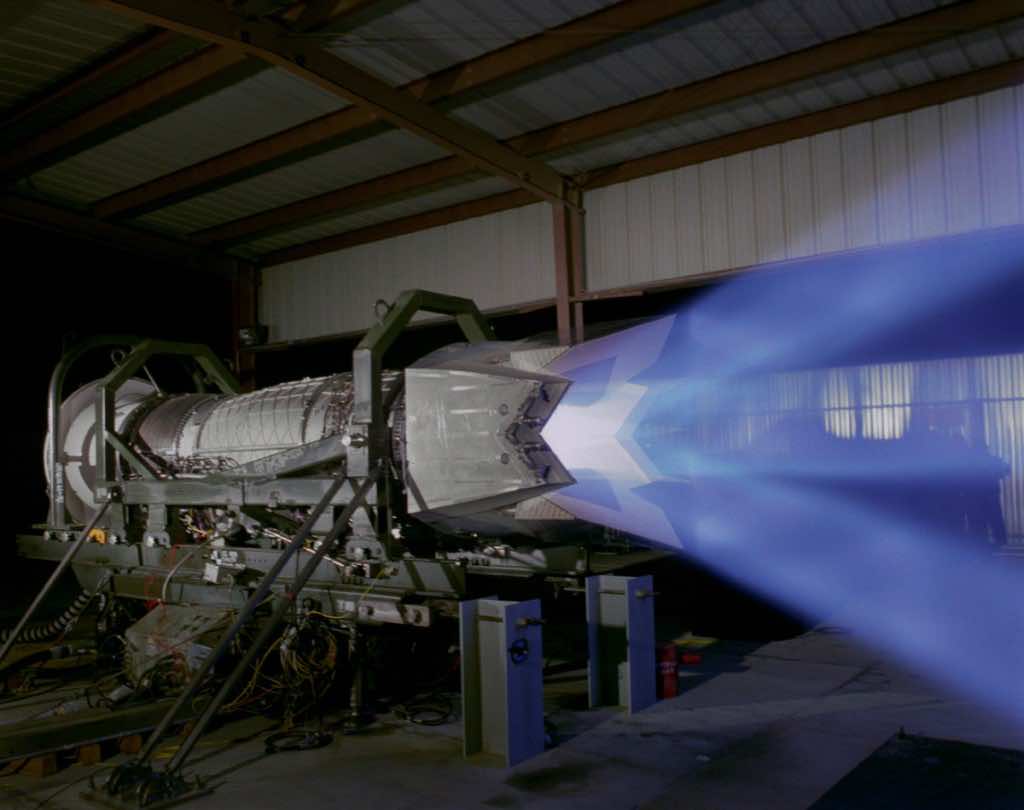

Thrust vectoring enables the pilots to fly up and over in a very tight arc, Wagemann says, and "gives us the nose authority to turn the jet while the wings are stalled, similar to a controlled.
Principle of thrust vectoring by fluidic injection (Reprinted from Ref.... Download Scientific

With the vector nozzle, the F/A-22 has a fourth type of control surface.. The F119 engines also give the F/A-22 a high thrust-to-weight ratio.That means the engines can actually handle many times the airplane's weight, allowing the plane to accelerate and maneuver very quickly.
A study on the thrust vector control using a bypass flow passage R Deng, HD Kim, 2015

Thrust vectoring, also known as thrust vector control ( TVC ), is the ability of an aircraft, rocket or other vehicle to manipulate the direction of the thrust from its engine (s) or motor (s) to control the attitude or angular velocity of the vehicle. In rocketry and ballistic missiles that fly outside the atmosphere, aerodynamic control.
Performance Analyses of Fluidic Thrust Vector Control System Using Dual Throat Nozzle AIAA Journal

Horizontal: T cos (c) - D = Fh. where sin and cos are the trigonometric sine and cosine functions. The thrust now appears in the vertical force equation. This allows the aircraft to climb faster than an aircraft without thrust vectoring and to execute sharper turns than an un-vectored aircraft. For moderate angles, the cos is nearly equal to.
Liquid Injection Thrust Vector Control Solid Rocket Thrust Vector

Thrust vector control systems that superimpose a side force on the motor thrust, steering being achieved by the side force causing a moment about the vehicle center of gravity are described. A brief review of thrust vector control systems is presented, and two systems, flexible joint and liquid injection, are treated in detail. Treatment of the flexible-joint thrust vector control system is.